
Impact Innovation: How to Evaluate, Design, and Develop Sustainable Digital Products
November 5, 2024
Impact Innovation: A holistic approach to sustainable change
Impact Innovation represents a unique opportunity to redefine how we conceive and develop products and services, generating value that goes far beyond economic benefits. Unlike traditional innovation, which typically focuses primarily on improving efficiency and competitiveness, Impact Innovation has a broader purpose: it actively seeks to enhance people's lives and protect the natural environment at every stage of design and development.
In the digital realm, this means creating technological solutions that are not only functional but also sustainable. This entails solutions that minimize their ecological footprint, promote social inclusion, and generate lasting value for all stakeholders involved. This approach considers the entire life cycle of a digital product, from the resources it consumes during development and operation to the social and environmental effects it produces. The goal is to ensure that every product we develop represents a positive advancement in every sense, creating a positive and lasting impact.

For businesses, Impact Innovation is an effective response to the growing demands for sustainability and social responsibility. It is not just about complying with increasingly stringent regulations; it is about aligning business objectives with the needs of society and the planet, generating digital products that contribute to the overall well-being and promote a more sustainable future.
In this context, the current Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) becomes particularly relevant—a regulatory framework that requires companies to report transparently and in detail about their social and environmental impacts. The CSRD drives accountability in business management, ensuring that sustainability is at the heart of all activities. For us, this regulation makes it imperative to evaluate, design, and develop digital products that are not only functional but also meet the expectations of regulators, customers, and society at large.
If you want to delve deeper into the implementation of the CSRD and explore the technological tools that can optimize the reporting process, you can access our Webinar on sustainability, AI, and automation for CSRD. In it, we will address strategies, work plans, and tools for creating reports aligned with this regulation, as well as answer your questions alongside experts in the field.
Criteria for evaluating the impact of a digital product
When one of our strategic goals is to maximize positive impact, it is essential to clarify our starting point and the destination we want to reach. This means defining a baseline that captures the set of data describing current conditions before implementing changes. This baseline should include:
-
Use of natural resources: Quantifying the resources consumed.
-
Effects on the ecosystem: Evaluating how the product affects the natural environment.
-
Pollution: Measuring the carbon footprint generated throughout the product's life cycle.
From this baseline, it is crucial to set objectives that address the environmental and social risks and opportunities associated with our economic activity. Conducting a competitive analysis can be valuable to understand how others are designing their products and how this may affect our market position.
Identifying the impact of digital products is also crucial, even if it may seem less evident. This impact encompasses everything from emissions generated by the energy required for development and maintenance to the water and carbon footprints of data centers, the hardware used, and the phase of software deactivation and disposal. For example, a study by The Shift Project revealed that one hour of streaming on Netflix generates approximately 36 grams of CO, and another report from Purdue University showed that one hour of video calling produces between 150 and 1,000 grams of CO, depending on video quality and infrastructure used.
GAIA Impact Index: Assessing the positive impact of technology
The GAIA Impact Index, an initiative we have developed in collaboration with the University of Valladolid, seeks to provide a structured and comprehensive framework for assessing the positive impact of technological products and processes. This index focuses on how technology can truly add value in areas such as environmental sustainability, social well-being, and economic growth.
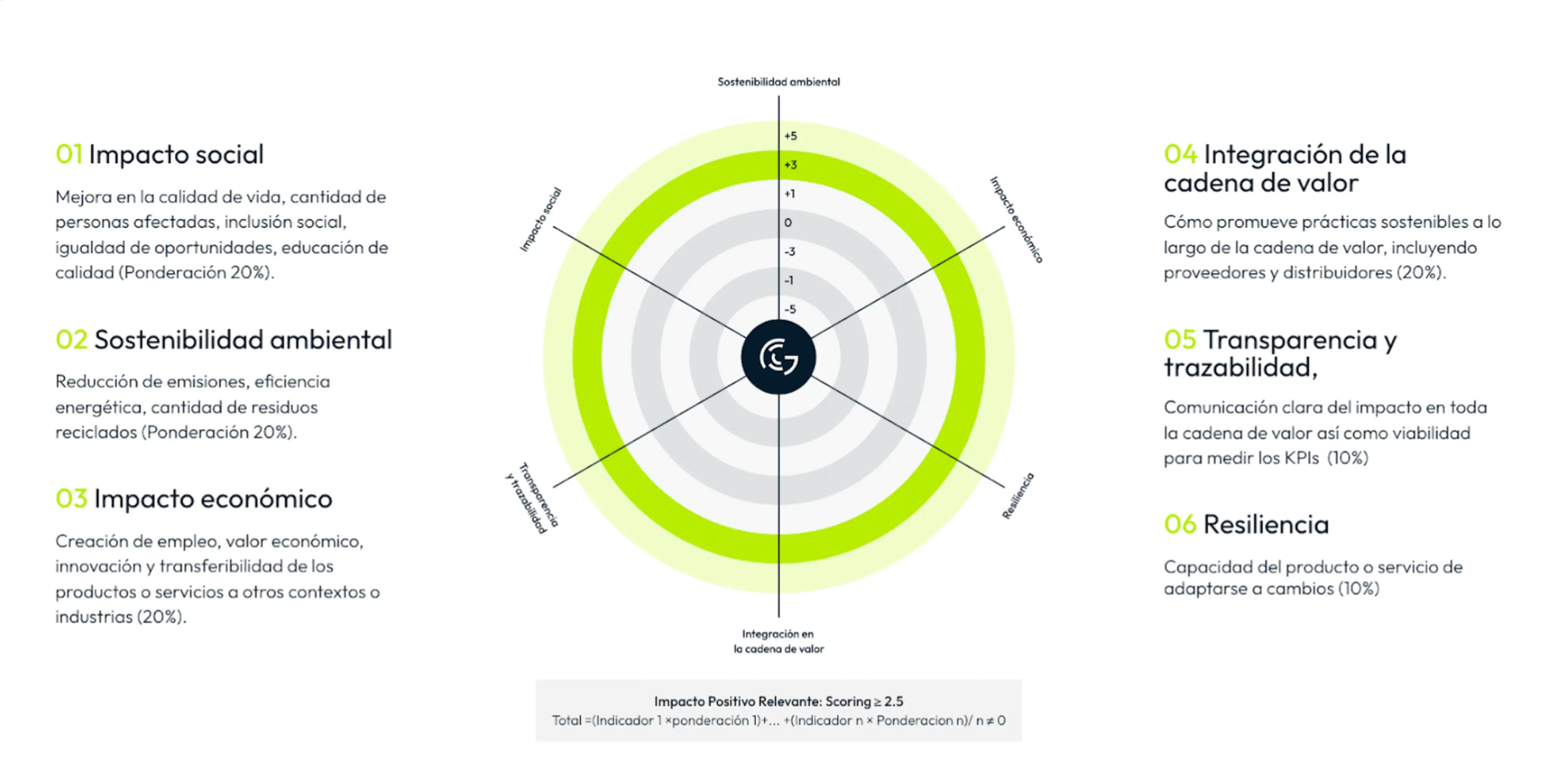
Here, I share the six key areas that make up the GAIA Index, which allow us not only to measure but also to maximize the benefits of our technological solutions.
-
Social impact: A digital product can have a significant impact on social inclusion and equal opportunities. For example, an educational platform that offers free or affordable access to specialized training.
-
Environmental sustainability: This aspect measures the impact in terms of emission reduction, energy efficiency, and resource recycling. Digital products can be optimized by migrating to servers powered by renewable energy or reducing code complexity to decrease resource usage.
-
Economic impact: In addition to their environmental and social sustainability, digital products can positively affect job creation and innovation. For instance, knowledge transfer in open-source software can be scaled to new sectors.
-
Integration in the value chain: This includes not only the company that develops the digital product but also its hardware, infrastructure, and service providers.
-
Governance and traceability: Having clear metrics that measure the impact of technological and process decisions, along with transparency policies and a clear governance structure, is essential. Especially now that reporting and auditing will be required.
-
Viability and resilience: Digital products must be capable of adapting to changes in technology and regulations. Implementing a flexible and efficient architecture is key to long-term sustainability.## How to Assess Initial Impact?
How to assess initial impact?
This process allows for identifying those areas that most influence the environment and society, laying the groundwork for prioritizing strategic improvements. From identifying critical areas and prioritizing the most relevant initiatives to implementing concrete improvements and monitoring their effectiveness, each phase is essential for building an innovation model that generates positive and tangible change.
1. Identification of critical areas
Based on the initial impact assessment, areas with the highest emissions are identified using a materiality matrix. This matrix visualizes the impact of different issues on the business and their relevance to stakeholders, such as employees, customers, regulators, and society at large. To evaluate and prioritize these areas, three key criteria can be considered: improving environmental efficiency, cost impact, and the value they generate for the customer and the business.
2. Prioritization of initiatives
Initiatives that present the greatest impact and viability are prioritized based on our strategic objectives.
3. Implementation of improvements
Once defined, innovation and transformation methodologies are applied to implement improvements that foster greater differentiation. This can include more efficient use of cloud infrastructure through auto-scaling, turning off inactive resources, using reserved instances, resource circularity, and optimizing data storage.
4. Continuous monitoring and adjustment
It is essential to measure and continuously monitor the effectiveness of changes in real time, adjusting strategies as necessary. To facilitate a quick analysis of the maturity status in sustainability and energy efficiency of your company, at SNGULAR we have developed a self-assessment that provides an initial diagnosis, helping to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
To allow you to conduct a quick analysis of the maturity status in sustainability and energy efficiency and resource usage in your company, at SNGULAR we have defined a self-assessment that offers a snapshot to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Conceptualization and design of sustainable digital products
How can we design or redefine a product based on the strategic objectives and the areas of greatest impact we have identified? To illustrate this process, I want to share the example of the B100 project, a 100% digital bank that we developed from scratch for our client Abanca. B100 was born with the purpose of changing the paradigm of the banking industry through the concept of "healthy banking," grounded in three pillars: financial health, personal health, and planetary health. As Jorge Mahía, Executive Director of B100, aptly states, “B100 was born from day one with a purpose: to promote a healthy and sustainable lifestyle.”
The implementation of this idea is based on the principles of Design Thinking by Tim Brown and David Kelley, along with the Lean Startup methodology by Eric Ries. This agile and iterative approach allows for customer feedback from the early phases, gathering real-world data and insights before fully committing to development.
To meet sustainability criteria, we employed the Planet-Centered Design methodology. This approach seeks to minimize negative impact while attracting new customers through sustainable innovations. The first step was to define a series of objectives and impact criteria, as well as conduct thorough research to understand market trends, customer needs, motivations, and environmental constraints. We defined the concept of sustainability and how to integrate it into an attractive financial proposal. Through qualitative and quantitative research methods, we identified the needs of potential customers via interviews, surveys, and focus groups.
As a result, we designed a digital app focused on the planet and people, promoting sustainability and financial health. B100 offers financial benefits to customers who maintain a healthy and active lifestyle, eliminating fees and providing an attractive interest rate. Additionally, a portion of the profits generated from card payments is allocated to the NGO Gravity Wave, which is dedicated to cleaning plastics from the ocean.
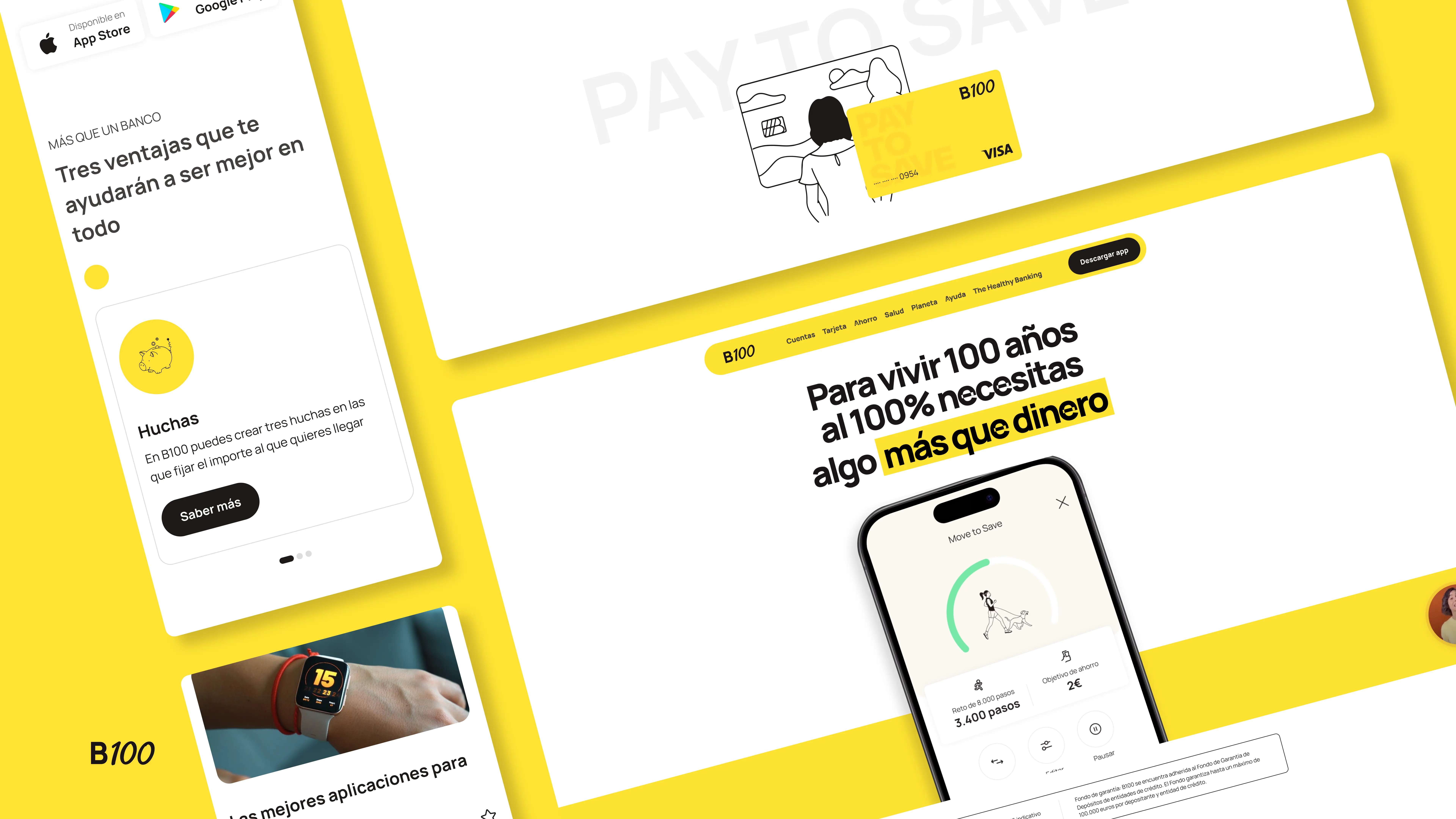
The B100 project was developed with efficiency as our mantra, achieving a lower digital impact. The result is an attractive and user-friendly application that offers all the functionalities of a state-of-the-art digital bank, with a design system oriented towards sustainability and features that help users achieve their savings goals. If you want to learn more about the B100 project in detail, you can see it here.
The B100 project drove us to develop design tools focused on sustainability, such as our Planet Centric Design Cards, which promote awareness and responsibility when conceptualizing products and services.

Our latest news
Interested in learning more about how we are constantly adapting to the new digital frontier?

Insight
October 22, 2024
CSRD Directive: Everything You Need to Know About the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive

Tech Insight
October 21, 2024
Overengineering in Software: How to Complicate Simple Things Unnecessarily

Tech Insight
October 14, 2024
PactFlow & Contract Testing: A Business Case Study


