
The European Accessibility Act (EAA): Towards a More Inclusive Digital Present
December 2, 2024
The Challenge of Digital Equality: Are We Truly Connected?
Nowadays, the use of digital devices is so embedded in our daily lives that we barely notice it. Sending a mobile payment, booking a hotel, purchasing a last-minute gift, or checking a bank balance are actions we take for granted. These technologies not only simplify daily tasks but have also become essential tools for fully participating in society. However, this reality is not the same for everyone. While many enjoy the convenience of the digital world, others face barriers we don’t even perceive.
In Spain, more than 4 million people live with some form of disability. This statistic takes on new significance when considering that, according to an e-government report, only 28% of apps are deemed accessible. This means millions of people face daily challenges accessing basic services that others use effortlessly.
This raises a crucial question: how inclusive is our digital world really? For a visually impaired person, a website without image labels can feel like a blank page. For someone with reduced mobility who struggles to use a mouse or touchscreen, navigating interfaces not optimized for keyboards can be virtually impossible. These digital barriers not only hinder access to essential services but also deepen inequalities in a society where digital technology is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
In this context, the European Accessibility Act (EAA) takes on special significance. More than just a legal obligation, this regulation is an invitation to reflect on and redesign how we conceive and use technology. Adapting our platforms and services is not merely a duty; it is an opportunity to ensure that everyone can benefit from a more accessible and equitable digital environment, addressing the needs of those who face barriers to accessing technology.
If you’re interested in learning how to create accessible digital products and understanding the challenges and opportunities of accessibility in technology design, don’t miss our webinar on accessible digital products. In this event, we explore how companies can comply with regulations and create more inclusive digital environments.
What Is the European Accessibility Act (EAA)?
The European Accessibility Act, adopted in 2019, is a European Union directive establishing clear requirements to ensure that certain products and services are accessible to all individuals, regardless of their abilities. It represents a critical step toward digital inclusion and lays the groundwork for businesses to adapt their services to the needs of a diverse population.
The EAA governs a wide range of products and services, such as:
• Technological products: ATMs, payment terminals, televisions, computers, and smartphones.
• Digital services: E-commerce, mobile apps, banking services, digitalized public transport, and emergency call accessibility (112).
The goal is to eliminate digital and physical barriers, ensuring everyone can fully participate in modern society.
How Can I Tell If the EAA Affects My Business?
The EAA has a broad scope, but not all businesses are required to comply. Here are some key points to determine if your business is within its reach:
Do You Offer Digital Products or Services?
This includes websites, mobile apps, and online services related to sectors like:
- E-commerce: Any e-commerce platform must meet accessibility standards.
- Banking services: Apps, financial management portals, ATMs, and payment terminals.
- Digitalized public transport: Ticket reservation systems, schedules, and real-time tracking apps.
- Audiovisual media: Platforms offering content like videos or streams must provide subtitles, transcripts, and accessible navigation.
- Emergency services: Access to 112 and related platforms.
Do You Operate in the European Union?
The directive applies to all businesses operating in EU member states, even if your headquarters are outside the EU.
Are You a Microenterprise?
If your business has fewer than 10 employees and an annual turnover under €2 million, you may be exempt from some requirements.
Although microenterprises are exempt in certain cases, adopting accessible practices is still a smart strategy. It not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also improves user experience for all, increases potential audience reach, and strengthens your business reputation. In an increasingly digital world, accessibility is not just an obligation but an opportunity to lead with responsibility and empathy.
EAA Implementation Dates:
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) sets specific deadlines businesses must consider to ensure compliance with accessibility requirements:
- June 28, 2025: From this date, all new products and services launched on the market must comply with accessibility standards.
- June 28, 2030: Products and services already existing before 2025 must be adapted to meet the regulations.
While this may seem like ample time, implementing accessibility measures can be a complex process requiring planning, technical adjustments, and training. Therefore, starting early is essential to avoid penalties, meet deadlines, and ensure a successful transition to a more inclusive digital environment.
Beyond legal implications, failing to meet accessibility standards can severely damage your company’s reputation, projecting an image of exclusion and lack of commitment to social inclusion. Conversely, ensuring accessibility not only builds trust and enhances brand perception but also significantly expands the reach of your products, making them accessible to a more diverse audience. This becomes a strategic lever that enhances usability, improves user experience, and maximizes the impact of your digital products.
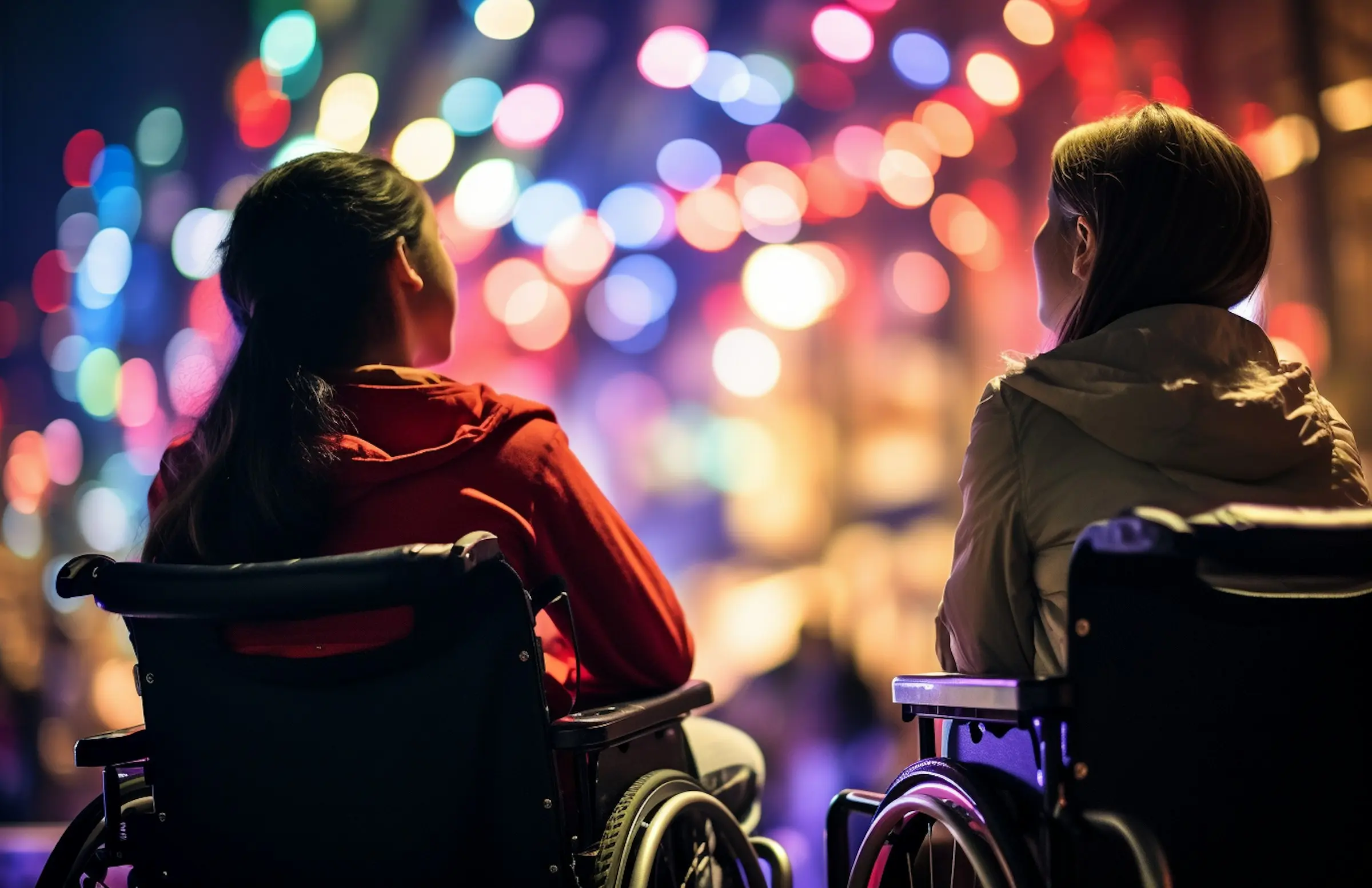

Criteria and Guidelines for Compliance with Accessibility Standards
To ensure digital products and services comply with the European Accessibility Act (EAA), companies must follow international accessibility standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), these guidelines serve as the primary framework for evaluating and improving digital accessibility.
1. Basic Accessibility Principles (POUR)
The WCAG are organized around four fundamental principles, known as POUR. Each addresses a key dimension of accessibility: 1. Perceivable: Information and interface components must be presented in a way that is perceivable to all users. Example: Providing alt text for images, subtitles for videos, and contrast options for users with visual impairments. 2. Operable: All interactive elements must be usable with various input devices, such as a keyboard, mouse, or assistive technologies. Example: Ensuring forms and buttons are keyboard-accessible and avoiding strict time limits for completing actions. 3. Understandable: Content and navigation must be clear and easy to comprehend for users of different skill levels. Example: Using plain language, providing clear instructions, and avoiding overly complex interfaces. 4. Robust: Content must be compatible with a wide range of user agents, including current and future assistive technologies. Example: Using well-structured semantic HTML code readable by screen readers.
2. WCAG Compliance Levels
The WCAG are divided into three levels of compliance companies can adopt depending on their needs and resources:
- Level A (minimum): Addresses the most basic accessibility requirements. Ensures users can access content but not always efficiently.
- Level AA (recommended): Provides a more comprehensive experience, eliminating most barriers for users with disabilities. This is the level required by the EAA.
- Level AAA (advanced): Guarantees the highest level of accessibility, but it is not always feasible to implement in all contexts.
Accessible Apps, Websites, and E-commerce
Under the EAA, digital products and services must be designed and developed following clear standards that remove barriers to access, promoting equal opportunities in the digital environment.
For mobile apps, this includes elements like keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and interfaces enabling intuitive and accessible touch interaction. On websites and e-commerce platforms, priority is given to content adaptability through magnification tools, high-contrast color schemes, and descriptive tags facilitating assisted navigation. These measures ensure that users with visual, auditory, or motor disabilities can independently search for information, complete forms, or make online purchases.
Implementing accessibility involves attention to structure, navigation, visual content, and interactive functionalities. Tools like Lighthouse or Axe, alongside manual tests using screen readers (VoiceOver, TalkBack, or NVDA), help identify and correct issues. Additionally, ensuring keyboard navigation and content scalability enhances usability.
Practical cases demonstrate that clear interfaces, descriptive tags, and adaptive navigation options benefit all users. Meeting these guidelines not only aligns products with European regulations but also broadens their reach, improves user experience, and strengthens companies’ reputations. Accessibility in apps, websites, and e-commerce is essential for an inclusive and competitive digital environment.
Accessibility Office: Driving Digital Solutions for an Inclusive World
The Accessibility Office is a specialized team committed to ensuring that web and mobile applications comply with accessibility regulations and standards. At SNGULAR’s Accessibility Office, we work alongside our clients to identify and eliminate barriers that hinder digital inclusion.
What exactly do we do? It all starts with a comprehensive audit, where we analyze applications from two perspectives: an automated approach, using tools that detect common issues, and a manual approach, diving into specific details thanks to our expertise and a checklist we’ve refined over the years. This enables us to identify both visible errors and more subtle ones. At the end, we deliver a report outlining the identified issues, solutions for addressing them, and a prioritization order.
We understand that fixing these issues isn’t always easy, which is why we also provide ongoing support. We help development teams prioritize tasks with a well-structured backlog and guide them in implementing solutions that not only address current issues but also prevent future ones.
Finally, we validate the improvements made. We repeat the analyses, both manual and automated, to ensure the applications meet accessibility standards. Additionally, we provide teams with tools and recommendations to maintain accessibility over time.
Our goal is not just to comply with regulations but to build a more equitable and accessible digital environment for everyone.
Our latest news
Interested in learning more about how we are constantly adapting to the new digital frontier?

Tech Insight
March 19, 2025
Visualizing Software Quality with JIRA, Google Sheets, and Looker
Insight
February 5, 2025
Pharmaceutical tenders: top 5 obstacles and how to overcome them

Tech Insight
January 13, 2025
How to bring your application closer to everyone

Tech Insight
December 19, 2024
Contract Testing with Pact - The final cheetsheet

